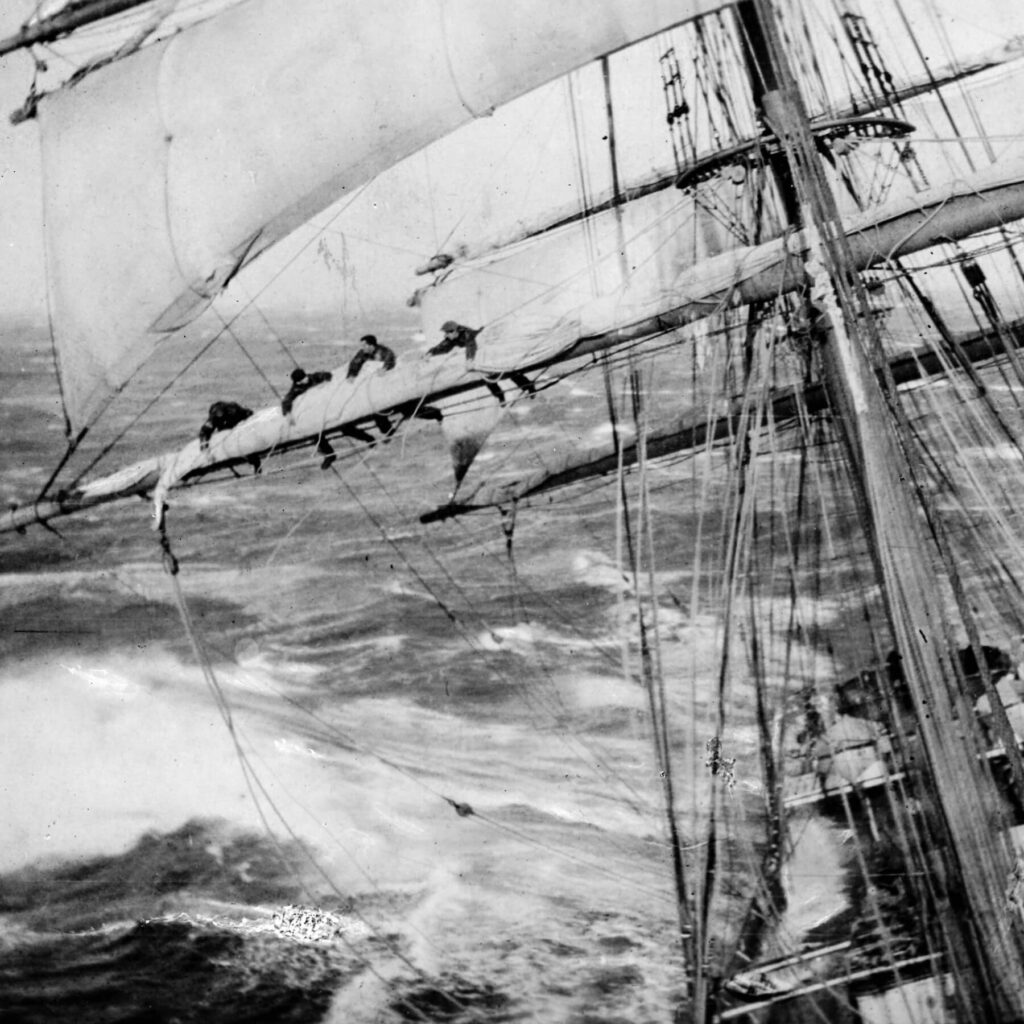
"History"
Originally, the term rigger was used to describe the people involved in rigging sailing vessels. When sailboats where no longer of importance for trading, riggers had to adapt and made the event industry as complex as possible so they would never run out of work again.



"Today"
Riggers are height workers in the event industry who are responsible of installing loads in stages or venues. These loads usually are lights, audio systems, video walls or anything needed for a show or any other event.
To fly these loads, trusses are used. Due to their modularity, nearly anything can be constructed with truss elements. Certain stage designs make it easy to see parallels with the LEGO technique.
The trusses are usually made of aluminum or steel profiles in the form of truss girders. Special electric chain hoists are used to raise and lower the elements, some of which weigh several tons.
Riggers hang the trusses to specific points under ceilings or in stages using chains, electric chain hoists, different steel elements and shackles.
Riggers always have to work safely and follow the industry standards to avoid any kind of damage.
An inspection by the structural engineer etc. is usually only carried out for very complex constructions.
Rigging is quite complex and can be devided in the following positions
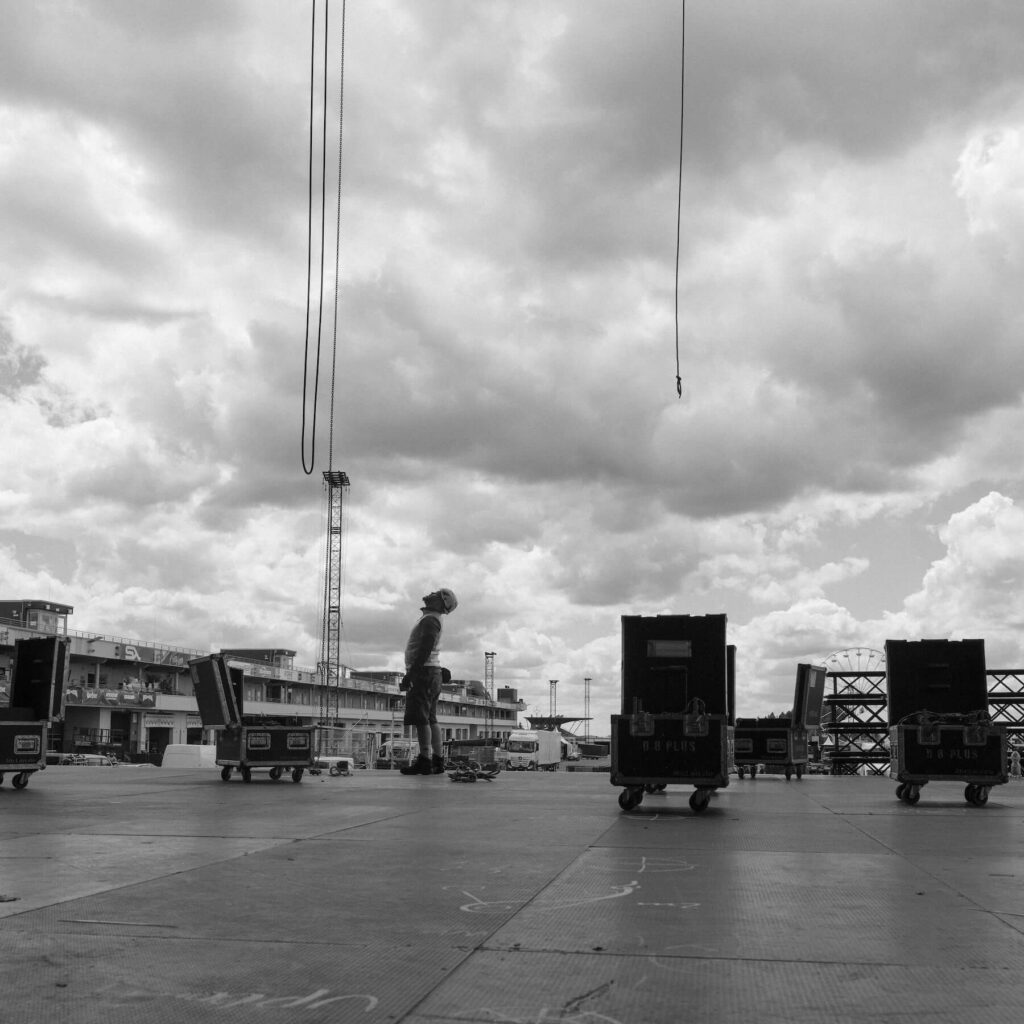
"The Grounder"
The grounder is an experienced rigger who supports the up-riggers from the ground. He shows the up-riggers where to install the motor chains. Most of the time by using a laser. He ties the up-riggers ropes to the motor chains or bridle legs.
The grounder is also alert and keeps people from working underneath the up-riggers. If working on two levels is necessary, the grounder lets everyone know to wear a helmet.
With his expertise he is always a step ahead and knows what is going on above and around him.


"The up-rigger"
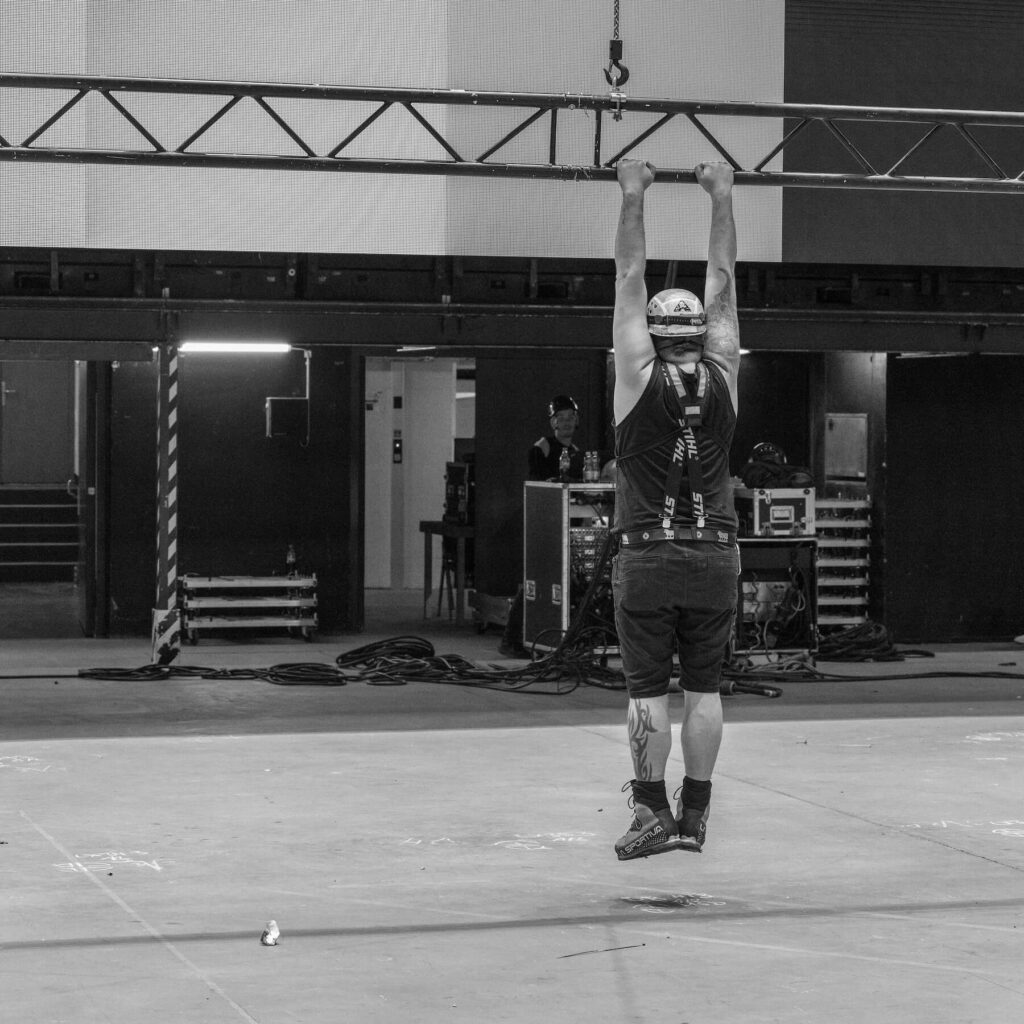
The up-rigger is usually a fit person who climbs on steel beams or on cat walks. Sometimes electrical lifts or cherrypickers are used to access the workspace. When arrived at the point where the motor chain or bridle leg is installed, the rigger uses a rope to pull up the typically heavy chains. Then he installs the motor chain or bridle leg safely.
Due to the up-riggers, work environment safety is the number one priority. To guarantee this, the rigger wears his safety equipment and is always attached to a lifeline or a safe structure.
"The controller guy"
The rigger on the motor controller is moving the chain hoists.
The bigger the system the harder the job. The controller guy has to communicate with all technical departments and fly their equipment according to their needs.
When working on big stages, these people sometimes look like the are working on a switchboard.
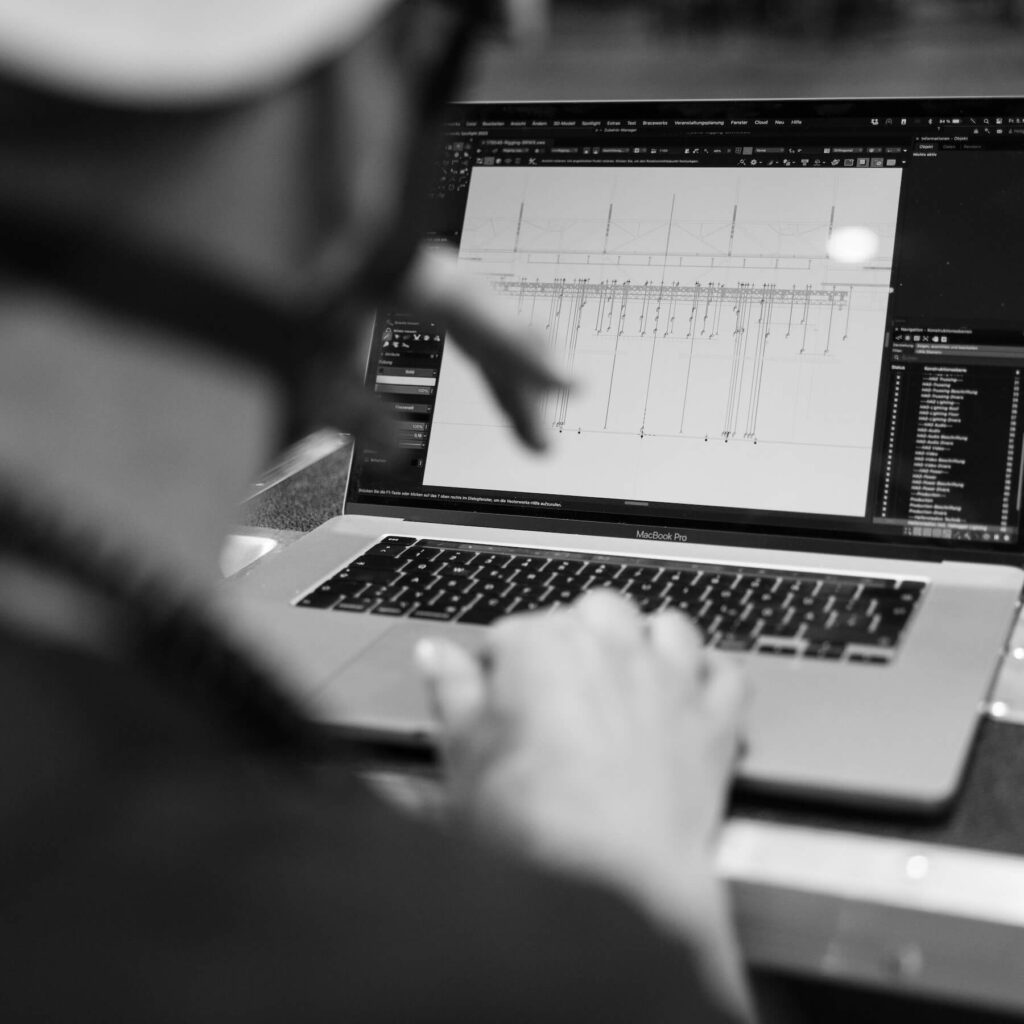


"The head-rigger"
This key position belongs to rigging experts. With their knowledge and experience, head riggers plan the rigging and organize the department. Rigging plans are often made with Vectorworks or similar CAD tools and help everyone understand what needs to be done.
Head riggers ideally are directly communicating with all key positions from the production and manage all riggers.